Demystifying the Mechanism of Pulmonary Ventilation

Pulmonary ventilation, often referred to simply as breathing, is an intricate physiological process that is essential for the survival of all vertebrates, including humans. It's a marvel of our biology, orchestrated by a series of intricate mechanisms working in harmony to ensure a constant supply of oxygen to our body's cells and the removal of carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism. In this comprehensive guide, we'll dive deep into the fascinating world of the mechanism of pulmonary ventilation, uncovering the intricacies that keep us alive and thriving.
Understanding the Basics of Pulmonary Ventilation
Pulmonary ventilation, in its simplest form, is the process of inhaling oxygen (O2) from the atmosphere and exhaling carbon dioxide (CO2) out of the body. This exchange is vital for maintaining the delicate balance of gases in our bloodstream. The mechanism of pulmonary ventilation involves several key components:
The Role of the Respiratory Muscles
Pulmonary ventilation wouldn't be possible without the orchestration of various respiratory muscles:
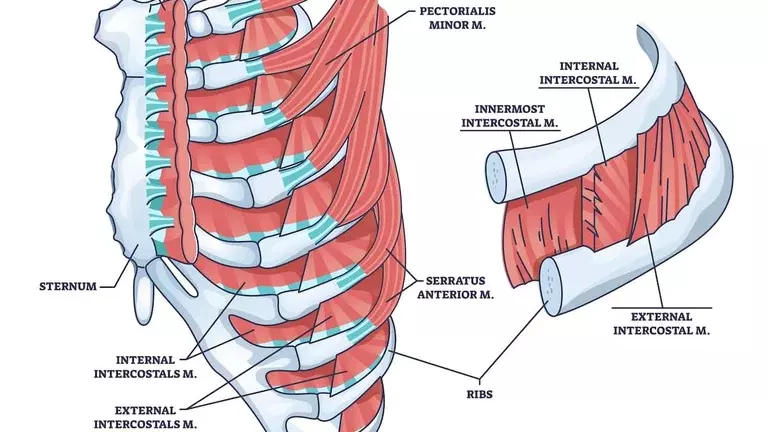
Introducing the Intercostal Muscles
The intercostal muscles, located between the ribs, assist in breathing by expanding the chest cavity when they contract. This expansion allows more room for the lungs to inflate with air.
Accessory Muscles for Labored Breathing
In situations where breathing becomes labored, such as during strenuous exercise, accessory muscles like the scalene and sternocleidomastoid come into play. These muscles help elevate the ribcage, further aiding in the inhalation process.
Factors Affecting Pulmonary Ventilation
Various factors can influence the mechanism of pulmonary ventilation:
Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors such as altitude, temperature, and air quality can affect how efficiently pulmonary ventilation works. At higher altitudes, for example, there is less oxygen in the air, requiring the body to adapt by increasing ventilation.
Health and Pathology
Certain medical conditions, like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), can impair pulmonary ventilation. Understanding these conditions is crucial for managing and improving respiratory health.
Emotional State
Emotions can also impact breathing. Stress and anxiety, for instance, can lead to shallow, rapid breathing, while relaxation techniques can promote slower, deeper breaths, improving overall ventilation.
The Significance of Pulmonary Ventilation
Oxygenation of Cells
Pulmonary ventilation ensures that our body's cells receive a constant supply of oxygen, necessary for energy production and overall function.
Removal of Carbon Dioxide
Efficient ventilation removes carbon dioxide, preventing its buildup, which can lead to respiratory acidosis, a potentially life-threatening condition.
Adaptation to Environmental Changes
Pulmonary ventilation allows us to adapt to changing environmental conditions, such as high altitudes or extreme temperatures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the mechanism of pulmonary ventilation is a complex yet beautifully orchestrated process that keeps us alive. From the rhythmic contractions of the diaphragm to the precise control of the brainstem, every element plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of gases in our bloodstream. Understanding pulmonary ventilation not only sheds light on the inner workings of our bodies but also underscores its significance in ensuring our health and well-being. So, the next time you take a deep breath, remember the intricate dance of mechanisms that make it all possible.